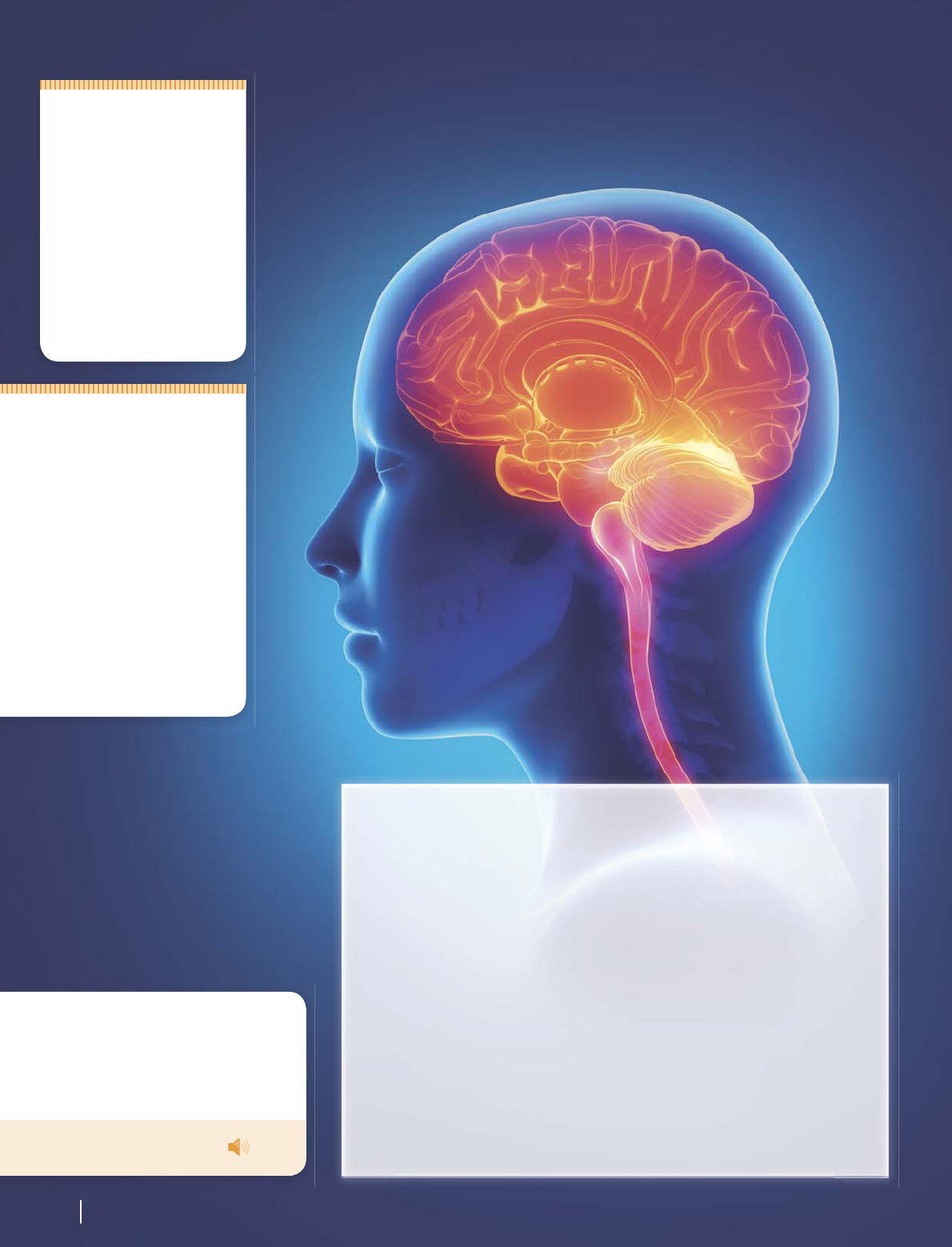
How does the brain process information?
Connected neurons form groups called
neural networks. The information from our
senses travels through neural pathways that
connect many neural networks within the
brain. For example, when you see an animal, the
information goes from your eye through the pathways
to a neural network that identifies the color of the animal. It
also goes through a network that identifies the type of animal it is,
and another that keeps memories of the animal. Now you can identify the
animal if you see it again. Your neurons form new connections and pathways
every time you learn something new or create a new memory.
When did all these changes happen?
The evolution of the human brain started millions of years ago. When early
humans began to walk upright, their brain size grew a little. Then for more than
a million years, humans moved to different parts of the world. They found
places with different plants, animals and weather. Humans had to learn many
things about their new environments. Their brains got bigger, too.
Thousands of years ago, there were important climate changes. During that
period, the human brain developed quickly and grew more complex. This step
in the evolution of human brains helped our ancestors survive. Their brains
helped them interact with each other and with their environments in new and
different ways.
There are still many questions about
the brain. Scientists still need to study it
to better understand how it works. But
we know the brain has evolved in many
ways over millions of years of history.
43Brain Evolution